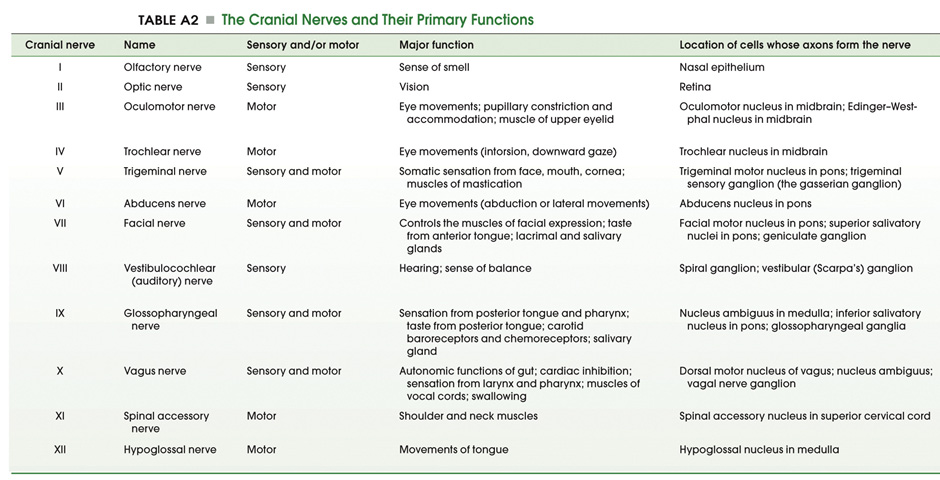
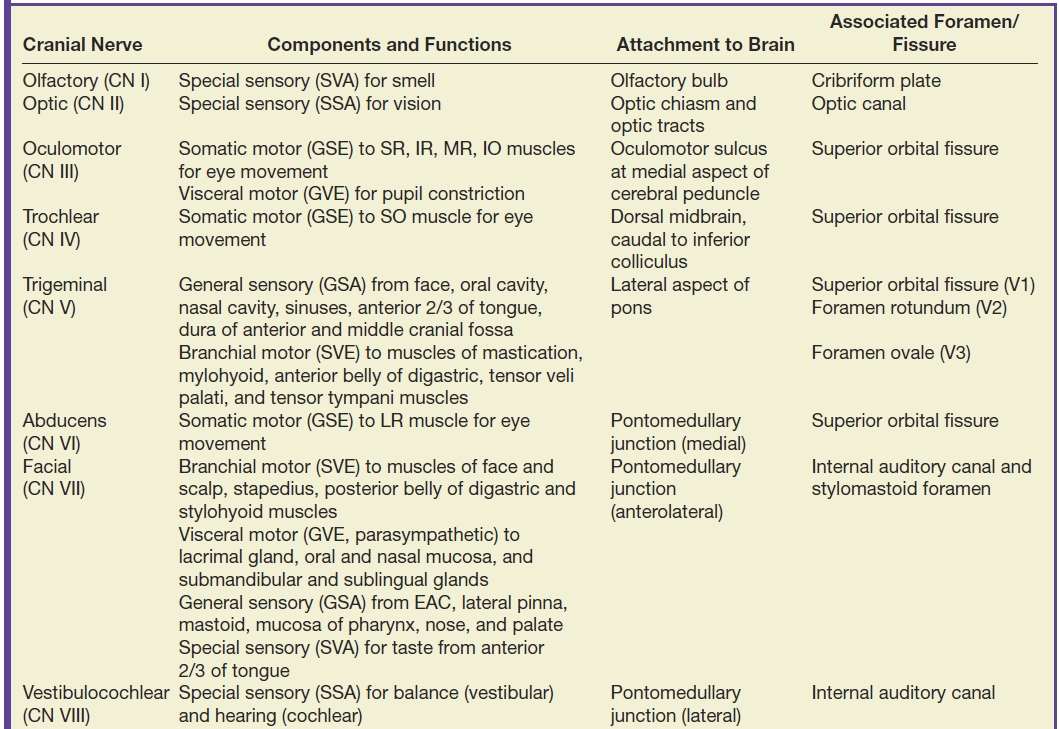
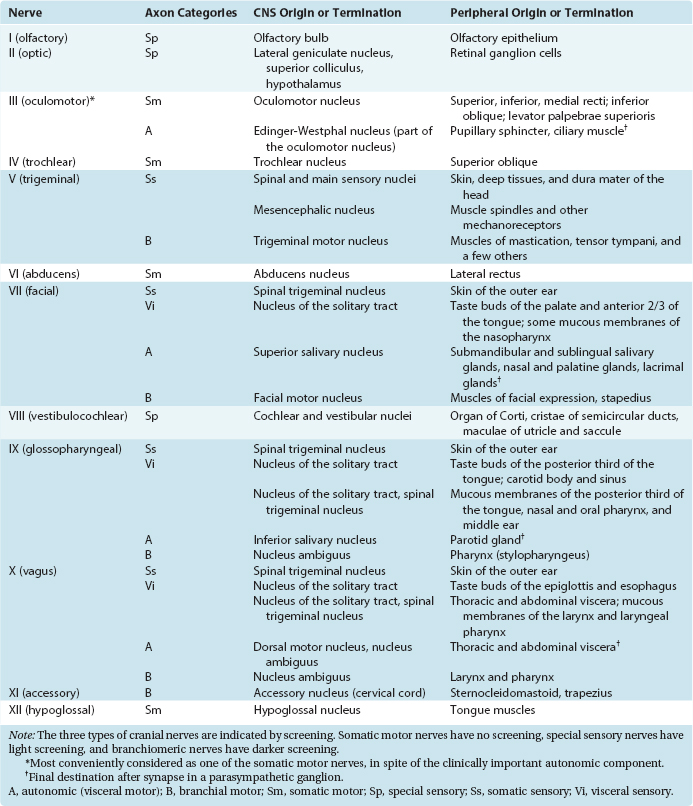
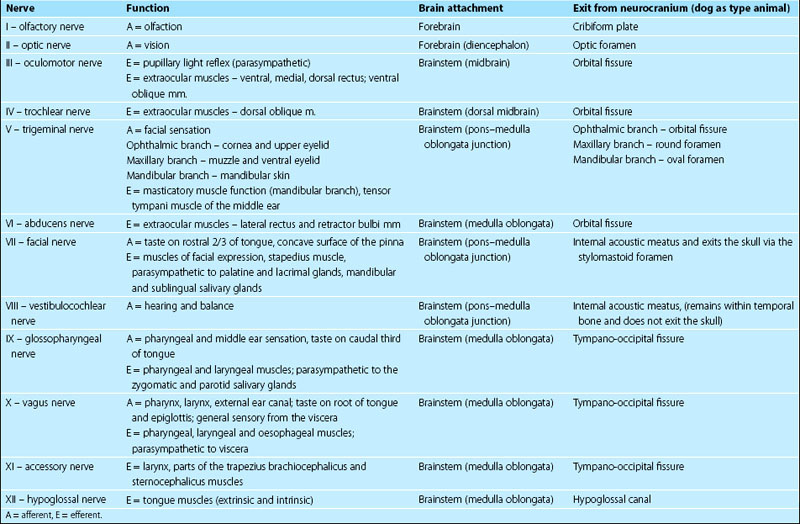
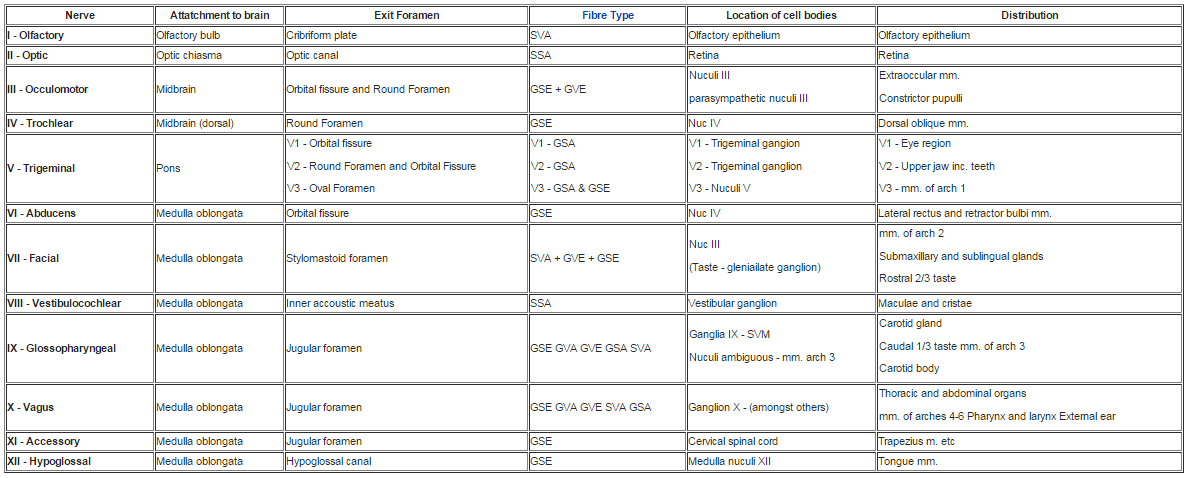
Cranial Nerves Location Table

Cranial nerve location and routes.
Cranial nerves location table. The cranial nerves are an important collection of nerves all of which travel directly to the brain rather than through the spinal cord like most other nerves. Cranial nerve malignant neoplasm malignant cranial nerve sheath tumors are uncommon and deals with weak prognosis as those of spinal nerves at other places. Motor cranial nerves help control muscle movements in the head and neck. Cranial accessory spinal accessory.
Facial nerve diseases this conditions pull down your facial expressions and cause weakness on your face. Controls the sternocleidomastoid and trapezius muscles and overlaps with functions of the vagus nerve cn x. The cranial nerves are nerves that arise from the brain and exit the skull through holes cranial foramina at its base rather than through the spinal cord. The names of the cranial nerves relate to their function and they are also numerically identified in roman numerals i xii.
For the fibre type please see the fibre type section heading 2 above using the fibre type link in the table. Cranial nerves are the nerves that emerge directly from the brain including the brainstem of which there are conventionally considered twelve pairscranial nerves relay information between the brain and parts of the body primarily to and from regions of the head and neck including the special senses of vision taste smell and hearing. Mainly motor cranial and spinal roots located in the jugular foramen. The cranial nerve functions are broken up into managing different aspects of your bodys daily tasks from chewing and biting to motor function hearing sense of smell and vision.
There are 12 of them each named for their function or structure. This nerve is involved together with nerve ix in the pharyngeal reflex or gag reflex. Scientists use roman. In this article we shall summarise the anatomy of the cranial nerves.
Your cranial nerves are pairs of nerves that connect your brain to different parts of your head neck and trunk. Peripheral nervous system connections with various organs and structures of the body are established through cranial nerves and spinal nerves. The first two nerves olfactory and optic arise from the cerebrum whereas the remaining ten emerge from the brain stem. The 12 cranial nerves are the abducent accessory facial glossopharyngeal hypoglossal oculomotor olfactory optic trigeminal trochlear vagus and vestibulocochlear nerve.
Each nerve has a name that reflects its function and a number according to its location in the brain.